Understanding Terpenes: What is Linalool?

- 1. What is linalool?
- 2. Where can you find linalool?
- 3. What are linalool's uses?
- 4. What are the health benefits of linalool?
- 4. a. Linalool for anxiety, depression, and stress
- 4. b. Linalool to reduce pain and inflammation
- 4. c. Linalool and alzeihmer's disease
- 4. d. Linalool as an antibacterial
- 5. What are some linalool rich strains?
- 6. The bottom line
When we smoke, vape or eat cannabis we're indulging many components found in cannabis plants and buds. Among these components, we can find the popularly known THC and CBD, the famous cannabinoids known for providing several benefits.
But THC and CBD aren't the only components in marijuana to come along with many benefits. Terpenes, for instance, are another type of compound present in weed buds that provide amazing effects, varying on each type of terpene themselves.
For example, linalool is one type of terpene, characteristic of the sweet, floral, sometimes minty, and woody scent and flavor in nature's plants and fruits. But this isn't everything that linalool is responsible for: it provides amazing health benefits as well.

Let's go through the properties of linalool terpenes in cannabis plants!
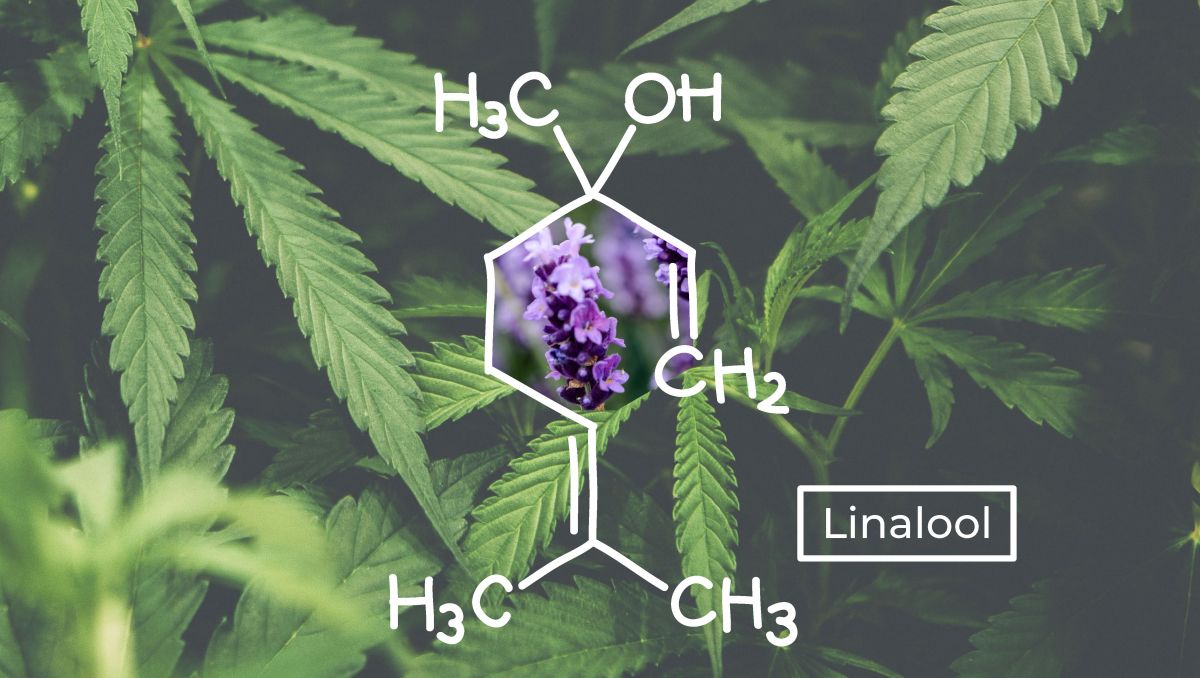
1. What Is Linalool?
As we've mentioned above, linalool (leen-uh-lool) is a part of the terpenes family in cannabis plants, that one characteristic of that sweet, floral, slightly citrus, and woody scent and flavor. But what is a terpene, you might wonder.
Terpenes are aromatic compounds found in marijuana plants, as well as in most other plants and fruits in nature, that give each plant their own particular smell and taste. There are more than 100 types of terpenes, and it's the combinations of these that give each strain their unique fragrance and set of properties.
In marijuana plants, terpenes are produced in the buds' trichomes, the shiny, transparent, mushroom-like glands where other cannabinoids such as THC and CBD are produced as well.
Linalool is a monoterpene that isn't among the most prevalent ones in cannabis plants. However, linalool is so commonly found in our everyday foods and drinks that it is believed that the average yearly consumption of linalool is of two grams per person.
2. Where Can You Find Linalool?
While linalool isn't part of the primary cannabis terpenes, this compound can be found abundantly in more than 200 hundred plants, such as lavender, laurel, spearmint, rosewood, mint, cypress, coriander, basil, and several more.1
| Aroma | Found in | Medical use | Effects | Vaporizes at |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Floral; minty; woody; spicy; citrus. | Lavender; laurel; spearmint; coriander; basil; rosewood; ginger; fungi; and more. | Depression; anxiety; Alzheimer's; Insomnia; pain; inflammation; and more. | Relaxing; sedative; stress relief; mood enhancement. | 197°C |
Linalool is also common in fungi and some fruits, such as tangerines, lemon, in nutmeg, ginger, black tea, thyme, sage, and more.
3. What Are Linalool's Uses?
Just like many of the other common cannabis terpenes, such as pinene and limonene, linalool emerged as a protection source for plants, to repel threatening predator insects and other external contaminations.
Therefore, it isn't uncommon for linalool to be one of the ingredients found in insecticides and repellents. Linalool-based insecticides can effectively kill or repel fruit flies, fleas, mosquitoes, and cockroaches.
On the other hand, given linalool is famous for its floral, minty, and woody hues of scent and flavor, you'll be able to find many different products in the cosmetics, cleaning, and aromatherapy section containing this terpene.
While lavender is typically thought of as a sedative and relaxing flower, it is in fact the linalool content in it that provides these effects. No wonder why many skin oils used for massages and meditation are lavender-scented.
Check the label behind any of your usual household products and it won't be surprising to find terms such as beta linalool, linalyl alcohol, or linalool oxide in the ingredients list. All these components are derived from linalool terpenes.
While some terpenes can trigger allergies on the skin when used in big amounts, this isn't the case for linalool. This terpene is a safe compound for topical application, in fact, you'll find it in many personal and skincare products, like shampoos, soaps, and lotions.
Products containing Vitamin E may also contain linalool, as it is a byproduct of linalool.
4. What Are The Health Benefits of Linalool?
Aside from being a great ally as an additive in foods, beverages, cosmetics, and cleaning products, linalool comes along with several health benefits, such as:
- Relieving anxiety and stress;
- Reducing inflammation and pain;
- Working as an antibacterial;
- Preventing neurodegeneration, and more.
Let's go through each of the properties of linalool.
Linalool for Anxiety, Depression, and Stress
Sadly there's no escape and animal testing seems to be still the most common method for scientific findings. For instance, one study performed on mice proved that linalool indeed provided a bigger state of relaxation in the rodents. 2
Furthermore, since linalool is a great sedative and relaxing component, it has also shown to be effective for the treatment of depression and for relieving stress.

In fact, linalool, as well as pinene terpenes, have been used as antidepressants by folk medicine for years already, boosting the levels of serotonin, dopamine and other neurotransmitters in the brain.
Linalool To Reduce Pain and Inflammation
Many studies back the fact that linalool is an effective treatment for pain and inflammation. On one hand, linalool relieves pain in three different ways:
- By targetting acetylcholine neurotransmitters in the brain, which is responsible for muscle movement;
- By reducing the excitability of the cells that transmit pain signals to the brain, known as spinal cord cells;
- And by controlling the heart rate, increasing the brain’s levels of adenosine.3,4,5
On the other hand, more studies performed on mice, sigh, have also found that linalool could aid in reducing inflammation.
Scientists found that this terpene inhibited inflammation in a mouse with acute lung injury, which makes linalool competent for treating inflammation.6
Linalool and Alzeihmer's Disease
A study led in 2015 on, guess what, mice have shown that linalool could also reverse neuropathological and behavioral impairments in brain cells caused by Alzheimer's disease. 7
However, more research needs yet to be done to affirm the possible qualities of linalool as a treatment for Alzheimer's.
Linalool as an Antibacterial
Given that most terpenes emerge as a defense measure for plants to prevent insects and other predators from attacking, it's no surprise to find that these terpenes are also effective antibacterials.

A study led in 2012 found that linalool had strong antimicrobial activity in the mouth, therefore, linalool-based toothpaste and gargling solutions are recommended to keep good oral hygiene. 8
5. What Are Some Linalool Rich Strains?
Once we have listed some of the benefits that you can get from consuming linalool terpenes, it only makes sense to wonder what cannabis strains contain the highest linalool contents. Let's find out.
You'll be able to find lots of linalool in the sweet hybrid Zkittlez Auto.
Users normally refer to this strain's flavor as a rainbow, with sugary candy and berry flavors, plus some mango, grapefruit, and chocolate-ish earthy hues.
6. The Bottom Line
There's no guilt in the pleasure of learning more about cannabis.
The more you know about marijuana plants, the different components that make each strain's characteristics, and the benefits each of them provide, the more control you'll have over your cannabis experience.
When you choose your strains with precision, you'll be able to enjoy exactly the effects, flavor, and fragrances you cherish the most!
EXTERNAL REFERENCES
- "Linalool" National Center of Biotechnology Information.
- "Anxiolytic and Anticonvulsant Effects on Mice of Flavonoids, Linalool, and α-Tocopherol Presents in the Extract of Leaves of Cissus sicyoides L. (Vitaceae)" Edvaldo Rodrigues de Almeida, Krissia Rayane de Oliveira Rafael, Geraldo Bosco Lindoso Couto, and Ana Beatriz Matos Ishigami. March 2009.
- "Linalool modifies the nicotinic receptor-ion channel kinetics at the mouse neuromuscular junction" L. Re, S. Barocci, S. Sonnino, A. Mencarelli, C. Vivani, G. Paolucci, A. Scarpantonio, L. Rinaldi, and E. Mosca. August 2000.
- "Linalool blocks excitability in peripheral nerves and voltage-dependent Na+ current in dissociated dorsal root ganglia neurons" José Henrique Leal-Cardoso, Kerly Shamyra da Silva-Alves, Francisco Walber Ferreira-da-Silva, Tiago dos Santos-Nascimento, Humberto Cavalcante Joca, Flávio Henrique Pequeno de Macedo, Pedro Militão de Albuquerque-Neto, Pedro Jorge Caldas Magalhães, Saad Lahlou, Jader Santos Cruz, and Roseli Barbosa. October 2010.
- "Involvement of adenosine A1 and A2A receptors in (-)-linalool-induced antinociception" Alessandra T. Peana, Paolo Rubattu, Gian Giorgio Piga, Silvia Fumagalli, Giampiero Boatto, Proto Pippia, and M. Graziella De Montis. April 2006.
- "Anti-inflammatory effects of linalool in RAW 264.7 macrophages and lipopolysaccharide-induced lung injury model" Journal of Surgical Research. January 2013.
- "Linalool reverses neuropathological and behavioral impairments in old triple transgenic Alzheimer's mice" Angélica Maria Sabogal-Guáqueta, Edison Osorio, and Gloria Patricia Cardona-Gómez. March 2016.
- "Antimicrobial effect of linalool and α-terpineol against periodontopathic and cariogenic bacteria" Soon-Nang Park, Yun Kyong Lim, Marcelo Oliveira Freire, Eugene Cho, Dongchun Jin, and Joong-Ki Kook. June 2012.













Comments