What is THC?

- 1. What are cannabinoids?
- 2. What is thc?
- 3. How to consume thc?
- 4. The effects of thc on our body
- 5. Medicinal uses
- 5. a. The 4 main benefits of medicinal cannabis use
- 6. How to intensify the effects of thc?
- 7. How to decrease the effects of thc?
- 8. How long does thc stay in the body?
- 9. In conclusion
Tetrahydrocannabinol is one of the 100+ cannabinoids found in cannabis plants and cannabis seeds. Most people know THC as the chemical compound in cannabis responsible for getting us high, but what more is there to know about this famous cannabinoid? THC doesn’t just get you high by accident. It works in a very intricate way within the human body. This mechanism doesn’t just underpin the quintessential cannabis high, but it determines how THC works as a medicinal molecule.
Interestingly, THC works like a key and specific receptors in our body are like a lock to that key. By mimicking compounds that our bodies create (more on those further down the page), this cannabis-derived molecule essentially “hacks” one of the most complicated systems in our body to produce changes in many different types of cells. Below, you’re going to learn everything you need to know about THC and how it works in the human body.
1. What are Cannabinoids?
Cannabinoids are known as being a secondary end product produced by the cannabis plant metabolism, which means these chemicals have no primary role in the plant’s development. However, they act as an immune system for the plant, protecting her against predators, parasites, and pests. These compounds are produced by cannabis flowers and can provide relief to a variety of symptoms like pain, nausea, anxiety, and inflammation. Cannabinoids imitate compounds our body naturally produces (named endocannabinoids) when there is an internal deficiency or problem.
These endocannabinoids make up a part of a larger signaling network called the endocannabinoid system. Known as the universal regulator of the human body, this network shows up just about everywhere. Researchers have found its components in the nervous system, digestive system, skeleton, muscles, skin, connective tissue, and elsewhere. But what is it doing in all of these places? Well, the endocannabinoid system helps all of the systems within the body stay in a place of biological balance, also known as homeostasis.
Let’s take the brain, for example. Most neurotransmitters travel from one neuron to the other by going from the presynaptic neuron to the postsynaptic neuron. In this model, neurons behind the others produce a chemical in order to send a message and change the way the neighboring neurons behave. However, endocannabinoids are able to travel backward across the synapse and change the incoming signals. Ultimately, they are able to dictate our brain chemistry and therefore our mood.
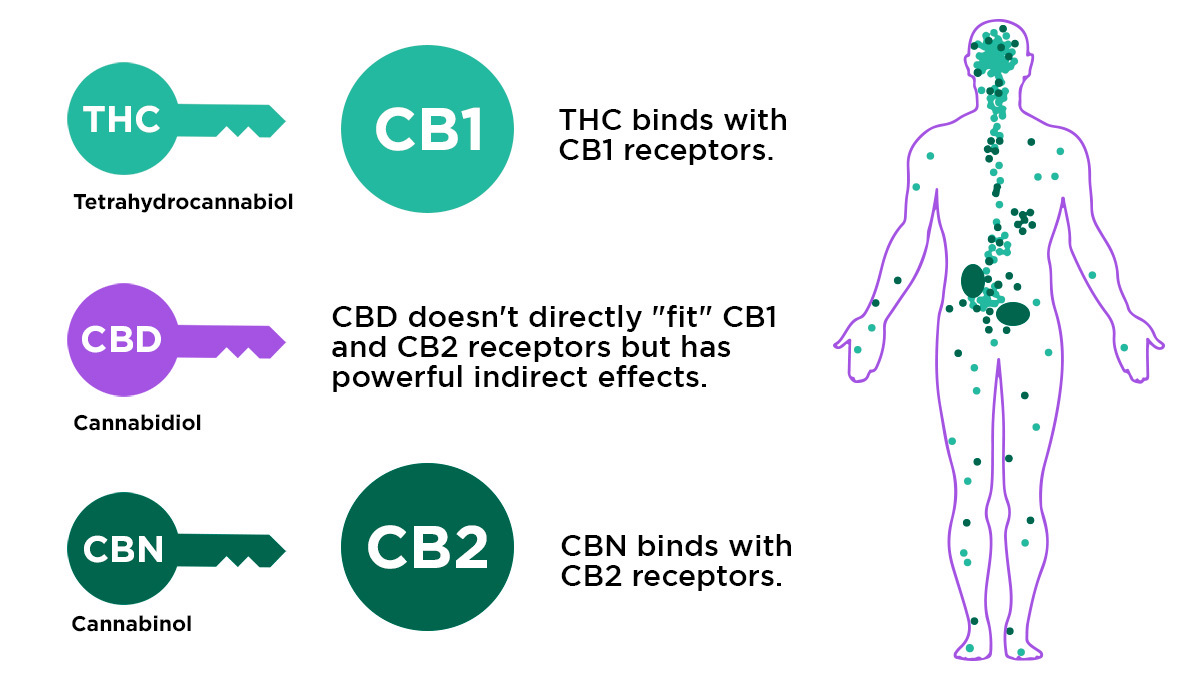
They play a pivotal role elsewhere in the body, such as in the remodeling of bone and the production of skin cells. But the endocannabinoid system consists of much more than our endocannabinoids. It also features receptors that these molecules bind to, as well as enzymes that build them and break them down. Scientists have also found that the endocannabinoid system forms only part of a much larger signaling network known as the endocannabinoidome. Some cannabinoids, including THC, are able to interact with receptors that make up this larger system. When cannabis is consumed, cannabinoids interact with cannabinoid receptors in our brain and depending on the cannabinoid, it will have a different effect on our body. For example, THC binds to receptors in our brain (that’s why it has a psychoactive effect), whereas CBN (a variation of CBD) binds to receptors scattered throughout the body (that’s why it provides pain-relieving and more of a couch-lock effect).
2. What is THC?
Delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (aka THC) like all other cannabinoids is a chemical product of the cannabis plants’ metabolism. It is found in high doses on cannabis flowers and the areas around them.
3. How to Consume THC?
No matter how you’re gonna consume THC, it all starts with decarboxylation. Live cannabis plants contain THCA, the non-active version of this compound. When cannabis is decarboxylated the acid molecule drops off and the THC is activated, this results in the effects we know. This means that the THC in fresh cannabis is not yet active. You can consume cannabis by smoking it in a joint (the most common method), by vaporizing it in electric vaporizers or in edibles. Edibles are a way of consuming cannabis without the need for heat (you’ll need to decarboxylate your cannabis before). After you decarboxylate it you can infuse active cannabis into any kind of food. Unlike smoking or vaporizing cannabis, when consuming edibles the cannabinoids will be released slowly and the high can last up to 6hrs, this method is usually recommended for medicinal users.
4. The Effects of THC On Our Body
THC stimulates cells in the brain to release dopamine, creating euphoria. It also interferes with how information is processed in the part of the brain responsible for forming new memories. THC can induce hallucinations, change thinking, and cause delusions.
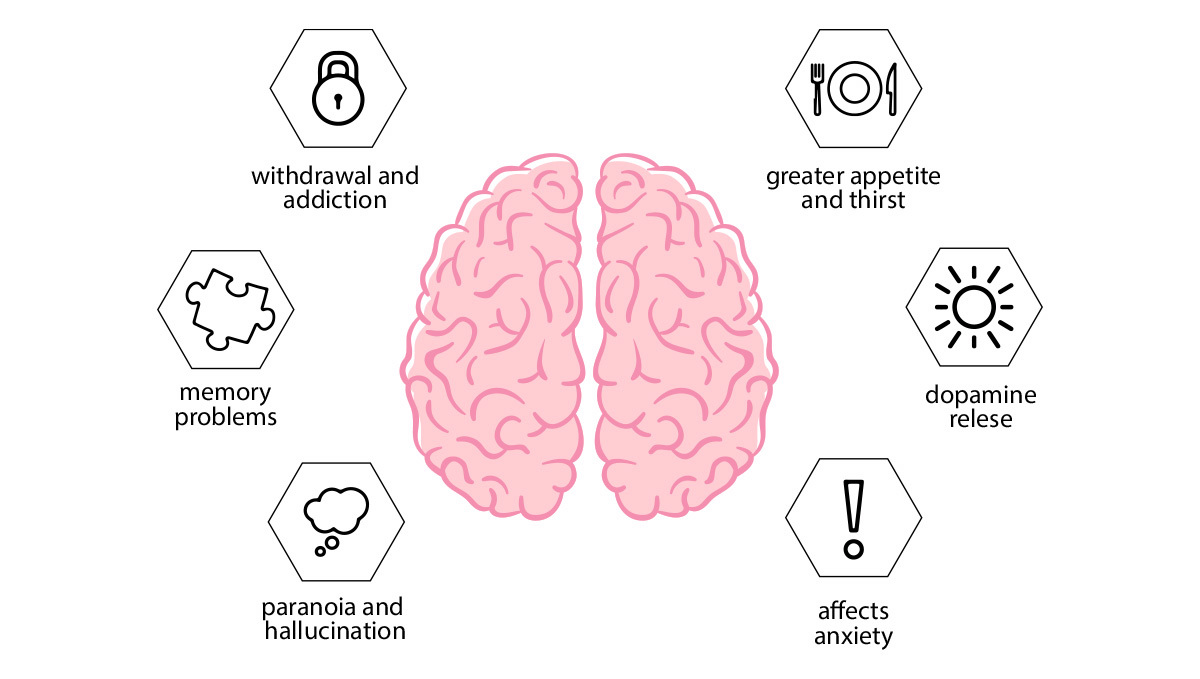
When smoking or vaporizing the effects last about two hours and can kick in 2-10 minutes after, if you decide to consume edibles the effect can last up to 8hs and the high can take up to 1hr to kick in. THC causes the cannabis high by latching onto CB1 receptors in the human brain. This action results in a sharp transient rise in dopamine—a feel-good neurotransmitter responsible for feelings of motivation and reward. Interestingly, THC mimics an endocannabinoid that our bodies produce called anandamide. This endogenous compound is released during exercise and likely underpins the euphoric sensations of the so-called “runner’s high”. Can you see the chemical parallels?
5. Medicinal Uses
THC can be extracted from cannabis or synthesized. When used properly THC can have many medicinal properties. It is used to treat or prevent nausea and vomiting associated with cancer medicine, increase the appetite of people with AIDS, and even may be able to improve memory when taken in small doses.
The 4 Main Benefits of Medicinal Cannabis Use
Thanks to the prohibition that cannabis has injured for the last 70 or so years, research is actually a fair way behind what many people may think. In many countries, it has been classed as a schedule one substance, which has severely limited researchers' access to cannabis. But now with the current wave of legalization, we are starting to see access increase and clinical studies are becoming more and more common. Although a lot of the data is still based on anecdotal evidence, there is a strong case for some emerging benefits.
Pain Relief
In the vast majority of countries and states where medical cannabis has been introduced, chronic pain relief is the number one reason for prescriptions. A recent study showed that up to 40% of patients who experience chronic pain found some sort of relief from cannabis usage. Cannabis is also an effective replacement for much stronger, and very addictive pain meds such as opiates and benzodiazepines (Valium and Xanax). One dispensary in Michigan has reported that up to 64% of their patients have been able to reduce, or totally cut out the use of opiate pain meds by replacing them with medicinal cannabis.
Reduction of Nausea and Increased Appetite for Chemotherapy Patients
One of the side effects of chemotherapy that can be most distressing for cancer patients is heavy nausea and lack of appetite. These side effects have a huge effect on the life quality of these patients, but thanks to medicinal cannabis there is some relief. Nabilone and dronabinol are two common drugs that contain THC and have been used for more than 3 decades to help chemo patients increase their appetite and treat nausea.
Sleep Improvement
For people suffering from insomnia, and other sleep disturbances, medicinal cannabis can make a huge difference. Not only does it help some patients with falling asleep much faster, but it can also help keep them asleep for longer periods. There is some evidence to show that THC usage can have a negative impact on REM sleep, but the positives can outway this negative depending on the patient's needs.
Reduction of Spasming Muscles in Paraplegics and Patients with Multiple Sclerosis
Patients who are suffering from MS (Multiple Sclerosis), and paraplegics often have issues with muscle spasms. These spasms can last for hours and can make life extremely uncomfortable. Certain recent studies have proven that THC usage can drastically decrease these spasms, which can bring huge relief to these patients.
6. How to Intensify the Effects of THC?
If you’re used to getting high and want a more potent high there are different ways to achieve this. You can smoke concentrates instead of flowers. Concentrates (like hashish and rosin) are made by extracting trichomes, this means you’ll be smoking solely on cannabinoids and terpenes.
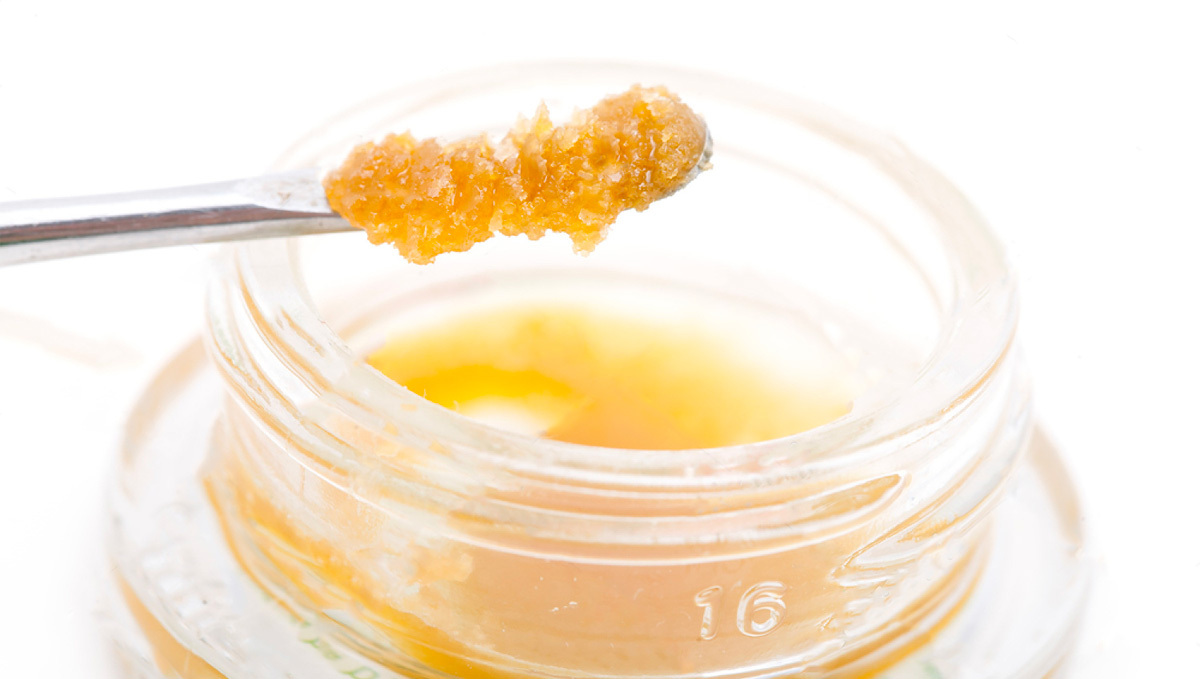

Concentrates can have up to 70% THC instead of up to 30% of cannabis flowers. The other way is to look for strains with terpenes (like Limonene and Terpinolene) that provide a more Sative type of high.
7. How to Decrease the Effects of THC?
Along with THC, cannabis produces another cannabinoid named CBD. This cannabinoid counteracts the effects of THC and can cut down the effects of paranoia, anxiety, and memory impairment associated with THC. CBD also provides a more medicinal type of high and can be used to treat pain and inflammation among other benefits.
8. How Long Does THC Stay in the Body?
This really depends on how often you consume cannabis, or other THC products, and which type of testing is administered. For infrequent users, the detection period should not be more than about 3 days (unless it is the hair that is being tested). For heavy users that number can be pushed out all the way to 30 days.
- Blood testing: 1 to 3 days for light users, 7 to 10 days for chronic users
- Urine testing: 1 to 3 days for light users, 30 to 50 days for chronic users
- Saliva testing: 24 to 48 hours for light users. 48 to 72 hours for chronic users
- Hair testing: 90 days for both light and chronic users
9. In Conclusion
If you’re looking for THC-rich strains, we have just the right thing for you. Gelato Auto has a crazy 26% THC level and it’s one of the most potent autoflowering strains available. It provides an uplifting and energetic high, great for the creative mind. If you’re not an avid smoker, we recommend Orange Sherbet Auto with 24% THC or Z Auto with 23% THC, these are also very potent strains that will deliver an uplifting and exhilarating high but will gradually lead to a relaxing body high.
With these strains you may want to take it slowly, these strains are powerful and not for beginners, too much THC can promote anxiety and panic attacks if you’re not used to it.














Comments